reading-notes
Reading notes about code for my future reference.
Javascript Programming Reading
###Control Flow
The control flow is the order in which the computer executes statements in a script.
(HOW THE PC READS CODE AND WHICH ORDER)
Example below:
The if function will go first followed by the else due to rules and conditional structures!
if (isEmpty(field)) {
promptUser();
} else {
submitForm();
}
Javascript includes many control structures and conditionals
-
Loops
-
Functions!
Parts of a script may also be set to start events when they happen!
Control structures can dictate flows of how code and script run. EVEN if they are only a few lines long.
Javascript Functions
Javascript function is a block of code designd to peform a particular task.
A javaScript function is executed when it gets trigged by something or called!
Function Syntax
A JavaScript function is defined with the function keyword, followed by a name, followed by parentheses ().
Names can contain letters, digits, under scores, and dollar signs (same rules as variables!)
Paratheses can include parameter names by seperating them with commas.
Function Invocation
The code inside the function will execute when “something” invokes (calls) the function.
- When an event occurs (when a user clicks a button)
- When it is invoked (called) from JavaScript code
- Automatically (self invoked)
Example of Function Returns
Why Use functions?
You can reuse code: Define the code once, and use it many times.
You can use the same code many times with different arguments, to produce different results.
Accessing a function without () will return the function object instead of the function result.
Functions Used as Variable Values
Function used as variable values!
Functions can be used the same way you use
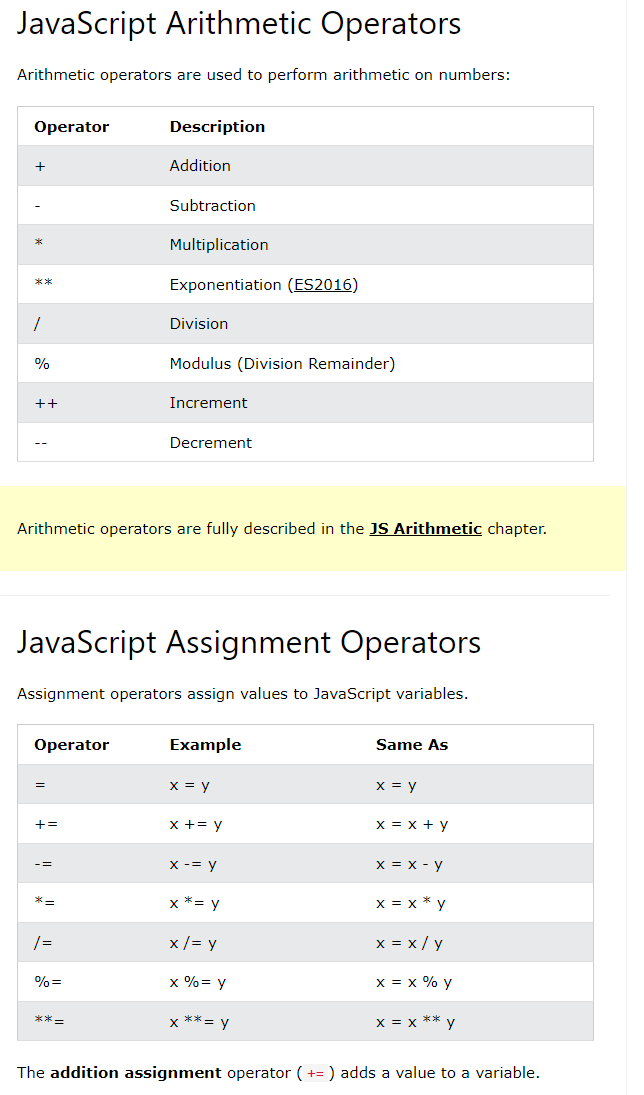
Types of Javascript Operators!
Assignment
let x = 10;
Adding let x = 5;
let y= 2;
let z = x+y;
Multiplying
let x = 5;
let y = 2;
let z = x * y;
JavaScript String Operators
The + operator can combine string!
let text1 = “John”;
let text2 = “Doe”;
let text3 = text1 + “ “ + text2;
Adding Strings and Numbers
let x = 5 + 5;
let y = “5” + 5;
let z = “Hello” + 5;
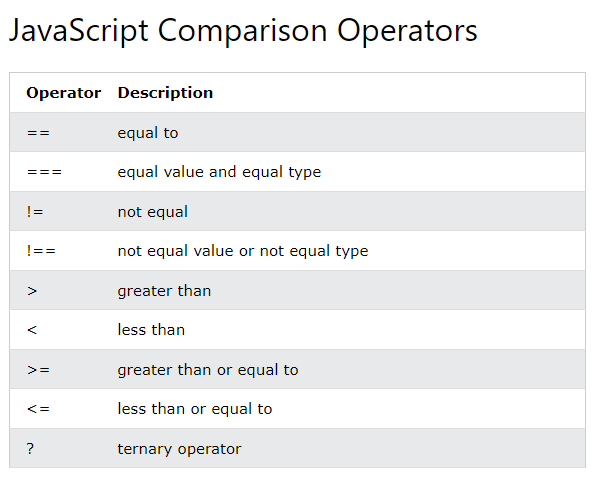
Javascript Comparison Operators